How Does an Amoeba Obtain Its Food: Essential Nutrition Insights
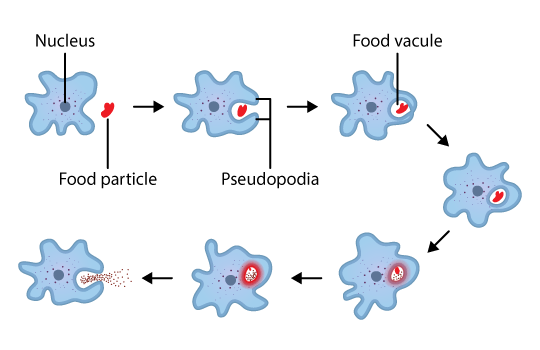
An amoeba obtains its food by using temporary extensions called “pseudopods” on the cell surface to engulf the food particle, forming a “food-vacuole.” Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones.
Amoebas are single-celled organisms that acquire energy by engulfing nutrients through a process called phagocytosis. The pseudopodia formed by the amoeba surround and engulf any food particle. Once the food is trapped, the amoeba secretes digestive enzymes to bring about digestion of the engulfed particle within the food vacuole.
By utilizing the flexible cell membrane and pseudopodia, an amoeba effectively collects and digests its food through the process of endocytosis. Understanding how amoebas obtain their food provides insight into their unique holozoic mode of nutrition and metabolic processes.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Contents
Introduction To Amoebas
An amoeba is a microscopic, single-celled organism belonging to the group of protozoans. They are found in diverse habitats such as freshwater, marine environments, and even in moist soil. Amoebas are known for their unique mode of obtaining food and survival mechanisms, making them a fascinating subject of study in the field of biology.
What Is An Amoeba?
An amoeba is a type of unicellular organism characterized by its shapeless, constantly changing body structure. They belong to the phylum Sarcodina and are known for their ability to form temporary extensions called pseudopods, which are essential for their movement and feeding.
Types Of Amoebas
There are various types of amoebas, each exhibiting distinct characteristics and behaviors. Some of the common types include Amoeba proteus, which is widely studied in laboratory settings, and Entamoeba histolytica, a parasitic amoeba known to cause amoebic dysentery. These amoebas showcase different adaptations and ecological significance.
Holozoic Mode Of Nutrition In Amoebas
An amoeba is a single-celled organism that obtains its food through a process known as holozoic nutrition. This mode of nutrition involves the ingestion of solid food particles through phagocytosis, followed by the digestion and absorption of nutrients. The holozoic mode of nutrition is essential for the survival and growth of amoebas, allowing them to obtain the energy and nutrients required for cellular functions.
Explanation Of Holozoic Mode Of Nutrition
The holozoic mode of nutrition in amoebas involves the ingestion of solid food particles, followed by the digestion and absorption of nutrients. This process is essential for the survival and growth of the organism, as it provides the necessary energy and building blocks for cellular functions.
Phagocytosis As The Process Of Obtaining Food
Phagocytosis is the process through which amoebas obtain their food. During phagocytosis, the cell extends pseudopodia to surround and engulf food particles, forming a structure known as a food vacuole. Digestive enzymes are then secreted into the food vacuole to break down the ingested food into simpler substances. The nutrients are then absorbed into the cytoplasm through diffusion, providing the necessary energy and building blocks for the amoeba’s cellular functions.
The Process Of Phagocytosis
An amoeba obtains its food through the process of phagocytosis. It uses temporary extensions called pseudopods to engulf and envelop food particles, forming a food vacuole. The complex substances in the food vacuole are then broken down into simpler substances, which diffuse into the cytoplasm.
Definition Of Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a vital process by which an amoeba obtains its food. It is a form of endocytosis where the pseudopodia, temporary extensions on the cell surface, surround and engulf food particles completely. This results in the formation of a “food-vacuole” within the amoeba’s cytoplasm.
Steps Involved In Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis can be broken down into several steps:
- Chemotaxis: The amoeba detects the presence of food particles through chemical signals and is attracted to them.
- Adhesion: The pseudopodia extend towards the food particle and attach to its surface.
- Engulfment: The pseudopodia continue to extend and envelop the food particle, completely surrounding it.
- Formation of the food vacuole: Once the food particle is completely engulfed, a food vacuole is formed within the amoeba’s cytoplasm.
- Secretion of digestive enzymes: The amoeba secretes digestive enzymes into the food vacuole to break down complex substances into simpler ones.
- Diffusion of simpler substances: The simpler substances resulting from digestion diffuse out of the food vacuole and into the amoeba’s cytoplasm.
- Residual body formation: Any waste materials that cannot be digested accumulate in a residual body.
- Exocytosis: The residual body is expelled from the amoeba’s cell through exocytosis, completing the process of phagocytosis.
Phagocytosis is a crucial process for amoebas, as it allows them to obtain the necessary nutrients for survival and growth. Through this process, amoebas are able to adapt and thrive in various environments.
Food Digestion In Amoebas
An amoeba takes in food using temporary extensions called pseudopods on the cell surface which envelop the food particle completely, forming a food vacuole.
Role Of Pseudopods In Engulfing Food
Amoeba ingests food through a process known as phagocytosis.
Introduction To Food Vacuoles And Its Function In Digestion
- The food vacuole is formed when pseudopods surround and engulf the food particle.
- Complex substances are broken down into simpler ones inside the food vacuole.
- Simple substances then diffuse into the cytoplasm for further processing.
Nutrient Absorption In Amoebas
In amoeba obtains its food through a process known as endocytosis. This involves engulfing food particles with the help of its flexible cell membrane, leading to the formation of a food vacuole. The engulfed food is then digested with the assistance of secreted digestive enzymes within the vacuole.
Diffusion As The Means Of Nutrient Absorption
In amoebas, nutrients are absorbed into the cytoplasm through diffusion. Complex substances from the food vacuole are broken down into simpler components, which then pass into the cytoplasm through the process of diffusion.
Transport Of Nutrients To The Cytoplasm
To ensure proper nutrient absorption in amoebas, the transport of these nutrients to the cytoplasm is essential. Once the nutrients have been simplified in the food vacuole, they are transported to the cytoplasm for utilization by the cell.
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Amoeba Obtain Food?
Amoeba obtains food through temporary extensions called pseudopods, which envelop the food particle, forming a food vacuole. Digestive enzymes break down complex substances into simpler ones, allowing them to diffuse into the cytoplasm. This process is called phagocytosis.
How Do Amoeba Protists Obtain Food?
Amoeba obtain food by using pseudopods to envelop food particles, forming a food vacuole. Digestive enzymes break down complex substances into simpler ones, allowing diffusion into the cytoplasm.
How Do Amoeba Ingest Food?
An amoeba obtains its food by engulfing it using temporary extensions called “pseudopods” on the cell surface. These extensions envelop the food particle completely, forming a “food-vacuole”. The food is then broken down into simpler substances, which diffuse into the cytoplasm.
How Does An Amoeba Collect Food For Energy?
An amoeba collects food by using pseudopods to engulf the food particle forming a food vacuole.
Conclusion
Amoebae, fascinating single-celled organisms, have a unique way of obtaining food. By extending temporary projections called pseudopods, amoebae surround and engulf food particles, forming a food vacuole. Inside the vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones, which then diffuse into the cytoplasm.
This process is known as phagocytosis and is essential for the amoeba’s nutrition. Understanding how amoebae obtain their food sheds light on the incredible adaptability and resourcefulness of these tiny creatures.